✍️ Author: Dr Eleni Christoforidou
Home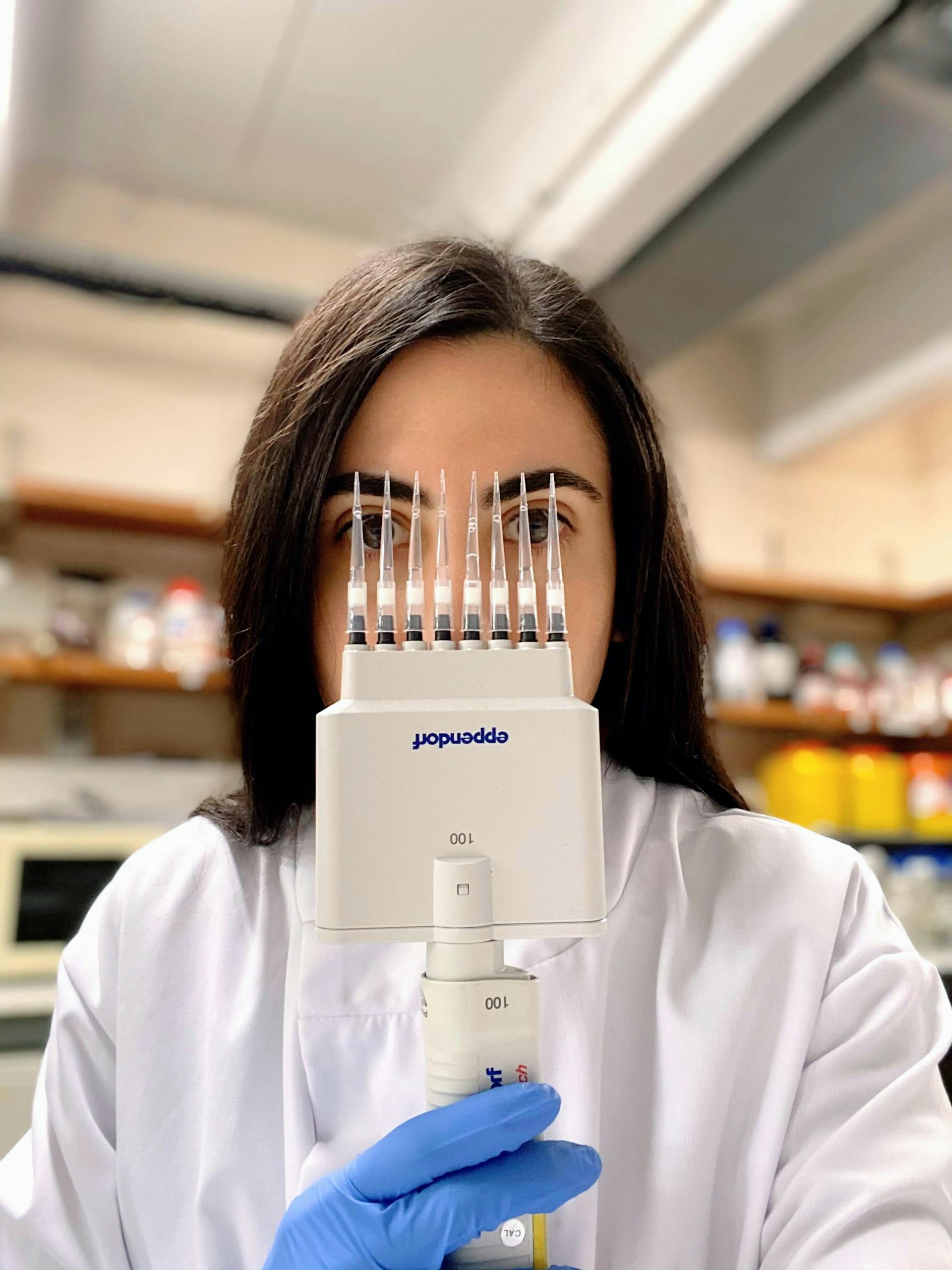
How NOT to hold a multichannel micropipette.
A Day in the Lab: Speeding up Pipetting
🕒 Approximate reading time: 4 minutes
Today's lab adventure was focused on the art of pipetting. Specifically, I utilised a multichannel micropipette to expedite a biochemical assay. This allowed me to simultaneously transfer solutions to eight wells on a plate. Then, for a bit of fun and education, I snapped the photo below demonstrating the absolute worst way to handle a multichannel micropipette during your experiments. To help you perfect your pipetting technique, I've also included a list of common errors and how to avoid them.

ANGLE: Maintain the pipettor in an upright position. Pipetting at an angle greater than 20º affects the internal pressure in the pipette tip, compromising accuracy as the angle steepens.
DEPTH: Avoid immersing the tip too deep into the liquid as it can cause droplets to form on the tip's side or create pressure changes that modify the volume. Conversely, shallow immersion can lead to air entering the tip.
SEAL: Ensure a good seal between the pipette tip and the pipettor. A poor seal can drastically impact volumes.
SPEED: Aspirating too quickly can introduce inaccuracies, especially with viscous liquids, and potentially lead to air bubbles or liquid contact with the pipette filter, raising the risk of contamination. Dispensing liquids too quickly can cause splatter or disrupt cells at the bottom of a plate.
CONTACT: Avoid touching the tips to the bottom of a well or tube while pipetting, as this can lead to incorrect liquid volumes due to tip opening blockage. Contact with the tips can damage cell health and impact imaging and reader performance by puncturing filter membranes or damaging optical surfaces on plates.
TEMPERATURE: Remember that most pipettors depend on air pressure to move liquids, and this air pressure is influenced by temperature changes. Therefore, prolonged use can cause heat transfer from your hand to the pipette, affecting the air between the piston and liquid, and subsequently making liquid transfers less accurate the longer the pipette is used.
Using a multichannel pipette is a fantastic way to increase efficiency in the lab. However, it's essential to master the technique to ensure accuracy and maintain the integrity of your samples. Happy pipetting!